
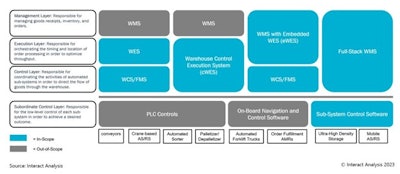
Warehouse automation software is used to control, execute and manage the operations of automated warehouses. Control software is focused on controlling the flow of goods through automated warehouses. This includes warehouse control systems which are used to control the flow of goods across fixed automation and fleet management systems which control the flow of automated mobile robots (AMRs) and automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
Execution software, on the other hand, is used to optimize workflows by controlling the timing and location of order processing. By optimizing order release timing, execution software is able to avoid bottlenecks by avoiding differential throughputs of upstream and downstream workflows. For example, by slowing down order release if the put-wall is flooded. Furthermore, the execution layer is used to avoid congested areas of the warehouse. For example, if the shuttle-system is operating at full capacity, the execution layer can direct pickers to the forward-pick area for manual picking.
 Interact Analysis
Interact Analysis
How the execution layer emerged
The execution layer emerged in response to two key trends:
1) the shift from “islands of automation”’ to “end-to-end solutions,” and
2) the transition toward waveless picking for omnichannel and e-commerce fulfillment.
End-to-end solutions
As automation becomes more advanced and more processes were able to be automated, the industry started to see more end-to-end solutions rather than islands of automation. The shift toward end-to-end solutions led to the need for better orchestration across multiple sub-systems. This was particularly true for the United States where the “pure-play integrator” model is far more common. These companies integrate disparate sub-systems, requiring a high degree of orchestration, which can be hard to achieve when dealing with equipment built by different manufacturers. This is because each manufacturer has their own communication protocol, and it can be difficult to get each system to communicate with one another. In Europe turn-key solutions are far more common whereby a single OEM/integrator is responsible for building and integrating the entire solution, making it easier to orchestrate and optimize the overall system. The “need” for an execution layer was less pressing in Europe because there was less friction in the communication between sub-systems, which is why much of the hype around warehouse execution systems (WES) has been limited to the United States.
Trend toward waveless picking
The second trend which led to the emergence of the execution layer is the transition toward waveless picking for omnichannel and e-commerce fulfillment. Prior to e-commerce and omnichannel retail, warehouse picking for wholesale and store replenishment was done using waves; groups of orders released to the warehouse at the same time. Typically, 2-4 waves were processed per day, and from an efficiency standpoint, the larger the number of orders grouped into each wave the better.
The emergence of omnichannel retail put pressure on the traditional wave methodology. If a direct-to-consumer order was received, it couldn’t be released to the warehouse until the previous wave was complete which could take several hours. It also made it difficult to expedite high-priority direct-to-consumer fulfillment which is often more profitable.
In addition to the difficulties associated with expediting priority orders, wave-based picking also led to inefficiencies during the order consolidation phase. This is because if the release of waves doesn’t match the rate at which batch-picked orders are consolidated downstream, bottlenecks and throughput constraints occur. Most warehouses that use wave-based picking release waves either periodically or once the previous wave has been complete. The problem with releasing waves periodically is that you can end up with bottlenecks if waves are released at a faster rate than the downstream consolidation. Conversely, waiting until the previous wave is complete before releasing a new wave can lead to the upstream pickers waiting idly whilst the downstream consolidation finishes.
How the execution layer enabled waveless picking
As the name suggests, waveless picking doesn’t use waves. Instead, individual orders are released to the warehouse based on the throughput of the downstream order consolidation. If, for example, downstream order consolidation slows down (e.g. if the put-wall is flooded), the waveless picking algorithm releases orders at a slower rate. Conversely, if downstream workflows are taking place at a rapid rate, the algorithm will release orders to the warehouse at a faster rate. Using the rate at which the downstream workflows occur to dictate the rate at which orders are released to the warehouse is referred to as a “pull” system because the downstream throughput is “pulling” the upstream order release.
In order to use waveless picking, you need to know the rate at which different workflows are happening since the order release timing is based on downstream throughputs. Early systems used approximations of these throughput rates to improve the order release timing. However, warehouse control system (WCS) vendors were able to collect accurate, real-time data on the throughput of various systems in the warehouse, such as automated sortation or put-to-light systems, allowing them to create high-efficiency waveless picking algorithms, becoming what’s described today as WES.
However, the benefits of a WES are not limited to just order release timing. Because the WES has visibility of the utilization (and thus, the throughput) of all automated systems, it can promote manual workflows if the automated systems are at full capacity. For example, if the shuttle-based automated storage retrieval system (AS/RS) is working at full capacity, it may direct pickers to the manual forward-pick area. Similarly if the automated sortation system is flooded, it may direct batch-picked totes to a manual put-wall.
The WES orchestrates the timing and location of warehouse workflows in order to optimize throughput.
1) it must be able to dynamically release orders to the warehouse based on the utilization status of the automation equipment.
2) it must be able to orchestrate multiple sub-systems, and 3) it must be able to orchestrate both man and machine (e.g. if the automated shuttle-system is at capacity, the system directs a manual picker to the forward pick area instead of using the shuttle system).
 Interact Analysis
Interact Analysis
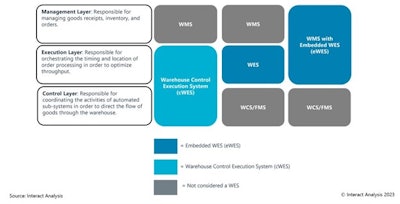
Types of WES
The first WES were developed out of existing WCS solutions because they had real-time visibility of the utilization of the equipment and could therefore control the order release timing based on system availability. In effect execution capabilities were “bolted on” to existing WCS solutions. These WES that “outgrew” WCS solutions as warehouse control execution systems (cWES).
However, a WES doesn’t need to control the automation in order to gain real-time visibility into the system availability. In many cases, the execution layer doesn’t actually control the automation at all. WES solutions that sit above the WCS are embedded WES (eWES).
Whilst most eWES solutions are truly “embedded” into the WMS, some can be sold as standalone solutions. If an eWES is sold as a standalone solution, it would therefore sit between the WCS and the WMS as an additional layer.
The argument for having a standalone execution is that most end-customers’ network of facilities have a heterogenous makeup of WMS and automation solutions. Using a standalone execution layer means that you’re not tied to a specific automation vendor or WMS provider, allowing the end-customer to have execution consistency across different facilities.




















