For food and beverage manufacturers and distributors, the adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and other automation technologies will become a defining factor for operational efficiency and market competitiveness. However, a significant challenge arises when manufacturers and distributors implement these technologies at different paces. The prevailing thought is that the adoption of AI should help smooth the bullwhip effect, but the different pace of adoption poses unique challenges to both the distributor and manufacturer from a data visibility, inventory management, and cash flow projection standpoint.
Data visibility between organizations is one of the underlying challenges, and the gap is amplified between a modernized organization and one that has technology debt. Manufacturers who leverage advanced AI for predictive maintenance, inventory optimization, and forecasting might find that distributors who have not adopted AI or advanced analytics struggle to interpret and react to AI-driven order information.
To fully gain the benefits of AI in a supply chain, both the distributor and the manufacturer need to be able to share data and logic built into their models. Information sharing between organizations should allow optimized inventory, better order tracking, and more accurate delivery lead times. In a worst-case scenario, the manufacturer starts using AI to improve their supply forecasting, but since the distributor is using static historical models, they may not leverage the new forecasting that results in an inventory imbalance and lost sales.
In an AI-driven operating model, data collaboration between organizations will become a crucial competitive advantage. Such initiatives include standardized data exchange protocols, shared training programs for workforce upskilling, and joint investment in technology upgrades. By aligning the pace of technology adoption, manufacturers and distributors ensure high data visibility, enabling a more responsive, resilient, and efficient supply chain capable of adapting to the dynamic demands of the food and beverage industry.
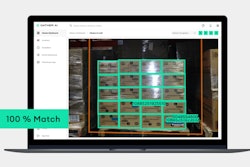
Improved data visibility and forecasting also unlocks opportunities for the food and beverage industry to optimize inventory management. AI and automation offer sophisticated solutions for real-time inventory tracking, predictive analysis for stock replenishment, and streamlined warehouse operations. AI models could significantly reduce waste associated with perishable goods, improve order accuracy, and ensure a steady supply of products to meet consumer demand. Additionally, automation in inventory management reduces the potential for manual errors and overhead costs, enabling employees to focus on more strategic tasks that add greater value to the business.
While benefits of implementing automation and AI to manage inventory are manifold, the impact is diminished if each company adopts these technologies within the silo of their own operations. Improved information sharing unlocks potential cash flow for all organizations involved and improves demand forecasting, especially if information is connected with market leading indicators. This then improves the accuracy of supply forecasting and reduces the likelihood of purchasing too much inventory. Right-sizing inventory would then unlock cash. Forecasting accuracy may also match supply and demand closer together, allowing for a leading organization to quickly adjust pricing to protect margins.
AI can also lead to improved management of receivables and payables to free up cash. On the receivables side, AI-enhanced analytics can identify customers with credit risk, help proactively follow up, and even suggest payment plans and approaches. On the payables side, AI helps maximize days payable outstanding by tracking the optimal balance of discounts and payment timing based on the unique financial situation of the organization at a moment in time. The payables process often has fraud risk, and AI could help detect potential fraudulent transactions and support management in fast decision-making.
The strategic application of AI and automation in inventory management and demand forecasting represents significant opportunities for the food logistics supply chain. By harnessing these technologies, the food and beverage industry can look forward to not just operational improvements but also enhanced financial performance, characterized by healthier cash flows and the agility to respond to market dynamics efficiently.
Best practices for implementation
Successful implementation of AI and automation in food logistics requires a clear strategy and technology vendors who align with business goals. Food and beverage manufacturers and distributors should define measurable objectives for their AI initiatives, focusing on areas that will deliver the highest value, such as inventory management, demand forecasting, and operational efficiency.
When evaluating solutions, make sure they are able to accommodate future growth demands yet flexible enough to adapt to changing market conditions and consumer buying patterns. This might involve choosing cloud-based AI platforms or modular automation technologies. Scaling AI technology involves a phased approach, expanding the implementation across the business slowly while continuously monitoring performance and making necessary adjustments.
Prior to full-scale implementation, conducting pilot tests of the AI solutions in a controlled environment is crucial. Pilot testing allows organizations to identify potential issues, gauge the effectiveness of the AI solution in a real-world setting and understand the impacts on current processes and workflows. Employee training and development is crucial during this phase to ensure users understand the principles behind the technology and how it can enhance decision-making and operational efficiency.
Since the benefits of AI and automation are maximized when information flows seamlessly between manufacturers, distributors and retailers, fostering partnerships and developing standards for secure data sharing and collaboration is essential. Joint investment in technology infrastructure can help synchronize the adoption pace across the supply chain while minimizing upfront costs for the adopters. This includes upgrading legacy systems to ensure compatibility and the ability to support advanced AI functionalities. By pooling resources through buying groups or associations, smaller distributors can overcome financial and technical barriers to technological upgrades, ensuring no entity is left behind in the digital transformation.
Taking the leap
Integration of AI and automation within the food logistics sector promises not just a revolution in how supply chains operate but also a substantial leap towards financial security and market agility. The key to successfully integrating these technologies lies not in ensuring immediate compatibility, but in cultivating an industry that values innovation, collaboration, and big-picture thinking. The adoption of AI and automation leads to a more effective and resilient supply chain, capable of adapting to fast-paced changes on a global scale. The future of food logistics, spearheaded by AI and automation, is not a distant prospect but an imminent reality that promises significant rewards for those ready to embrace it.