The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the U.S. Department of Transportation’s National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) jointly finalized standards for medium- and heavy-duty vehicles that will improve fuel efficiency and cut carbon pollution, while bolstering energy security and spurring manufacturing innovation. The final phase two standards were called for by President Obama’s Climate Action Plan, and respond to the President’s directive in early 2014 to develop new standards that run into the next decade.
The final phase two program promotes a new generation of cleaner, more fuel-efficient trucks by encouraging the wider application of currently available technologies and the development of new and advanced cost-effective technologies through model year 2027. The final standards are expected to lower CO2 emissions by approximately 1.1 billion metric tons, save vehicle owners fuel costs of about $170 billion, and reduce oil consumption by up to two billion barrels over the lifetime of the vehicles sold under the program. Overall, the program will provide $230 billion in net benefits to society, including benefits to our climate and the public health of Americans. These benefits outweigh costs by about an 8-to-1 ratio.
The final standards are cost effective for consumers and businesses, delivering favorable payback periods for truck owners. The buyer of a new long-haul truck in 2027 would recoup the investment in fuel-efficient technology in less than two years through fuel savings.
“The actions we take today on climate change will help lessen the impacts on future generations,” said EPA Administrator Gina McCarthy. “This next phase of standards for heavy- and medium-duty vehicles will significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions while driving innovation, and will ensure that the United States continues to lead the world in developing fuel-efficient technologies through the next decade and beyond.”
“Today’s ambitious but achievable announcement is a huge win for the American people, giving us cleaner air, more money saved at the pump, and real benefits for consumers across the supply chain,” said Transportation Secretary Anthony Foxx. “Today’s action preserves flexibility for manufacturers to deliver on these objectives through a range of innovations and technology pathways.”
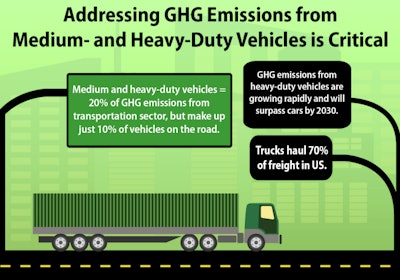
Heavy-duty trucks are the second largest segment and collectively make up the biggest increase in the U.S. transportation sector in terms of emissions and energy use. These vehicles currently account for about 20 percent of GHG emissions and oil use in the U.S. transportation sector. Globally, GHG emissions from heavy-duty vehicles are growing rapidly and are expected to surpass emissions from passenger vehicles by 2030. Through the Paris climate agreement and discussions with other countries, the United States is working with other major economies to encourage progress on fuel economy standards, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions that will improve global energy and climate security by reducing our reliance on oil.
The product of four years of extensive testing and research and outreach to industry, environmental organizations, labor unions, and other stakeholders, the vehicle and engine performance standards would cover model years 2021-2027, and apply to semi-trucks, large pickup trucks and vans, and all types and sizes of buses and work trucks. These standards will result in significant GHG emissions reductions and fuel efficiency improvements across all of these vehicle types. For example, when the standards are fully phased in, tractors in a tractor-trailer will achieve up to 25 percent lower CO2 emissions and fuel consumption than an equivalent tractor in 2018.
The agencies are also finalizing fuel-efficiency and GHG standards for trailers for the first time. The EPA trailer standards, which exclude certain categories such as mobile homes, will begin to take effect in model year 2018 for certain trailers, while NHTSA’s standards will take effect as of 2021, with credits available for voluntary participation before then. Cost effective technologies for trailers – including aerodynamic devices, lightweight construction and self-inflating tires – can significantly reduce total fuel consumption by tractor-trailers, while paying back the owners in less than two years due to the fuel saved. Recognizing that many trailer manufacturers are small businesses, the program includes provisions that reduce burden, such as a one-year delay in initial standards for small businesses and simplified certification requirements.
Compared to the proposal, the final program:
- Achieves 10 percent more GHG and fuel consumption reductions;
- Has more robust compliance provisions, including improved test procedures, enhanced enforcement audits and protection against defeat devices;
- Includes more stringent diesel engine standards
- Improves the vocational vehicle program with a regulatory structure better tailored to match the right technology for the job;
- Maintains the structure and incremental phase-in of the proposed standards, allowing manufacturers to choose their own technology mix and giving them the lead time needed to ensure those technologies are reliable and durable.
NHTSA and EPA have worked together to harmonize their standards under this program. The agencies have worked closely with the State of California’s Air Resources Board in developing and finalizing the standards. All three agencies are committed to the goal of setting harmonized national standards. Throughout every stage of development, this work has benefited from a collaborative dialogue with industry, labor and environmental organizations. For example, this feedback has improved the agencies’ ability to measure industry performance and enforce compliance for both full vehicle and engine standards.
Today’s final rulemaking builds on the fuel efficiency and GHG emissions standards already in place for model years 2014-2018, which alone will result in CO2 emissions reductions of 270 million metric tons and save vehicle owners more than $50 billion in fuel costs. Truck sales were up in model years 2014 and 2015, the years covered under the first round of truck standards.
The rule also builds on standards that the Administration has put in place for light-duty vehicles, which are projected to reduce carbon pollution by billions of tons of over the lifetime of vehicles sold, and will save consumers money at the pump.
For more details on DOT’s and EPA’s phase two greenhouse gas emissions and fuel efficiency standards for medium- and heavy-duty vehicles, visit: https://www3.epa.gov/otaq/climate/regs-heavy-duty.htm and http://www.nhtsa.gov/fuel-economy















