The influx in cargo theft, cybersecurity concerns and ever-changing industry regulations continue to threaten the safety and security of tomorrow’s supply chains.
But, when it comes to the State of the Supply Chain, the implementation of technology mixed with the ability to be flexible, nimble and versatile will enable the logistics world to pivot accordingly.
Marina Mayer, editor-in-chief of Food Logistics and Supply & Demand Chain Executive, talks exclusively with Jim Bresler, director of product management, food and beverage, Plex by Rockwell Automation, about why companies need to adapt to ongoing predictable supply chain disruptions in order to succeed in the New Year.
CLICK HERE to read the article in full.
Food Logistics: From your perspective, what are considered the Top 5 trends to watch in 2024? And why?
Jim Bresler:
Sustainability. Cold food supply chain companies are also focusing on reducing their environmental impact. This is being driven by consumer demand, government regulations, and the rising cost of energy. Companies are implementing sustainable practices such as using renewable energy, reducing waste and using eco-friendly packaging materials.
Robotics and automation. Robotics and automation are being used in the cold supply chain industry to improve efficiency and reduce costs. For example, robots can be used to pick and pack goods and automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) can be used to manage inventory.
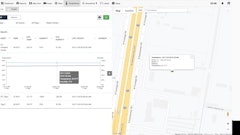
Digital transformation. Cold food supply chain companies are increasingly investing in digital technologies to improve efficiency, visibility and traceability. This includes technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), big data analytics and the Internet of Things (IoT). For example, AI can be used to predict demand, optimize transportation routes, and identify potential disruptions.
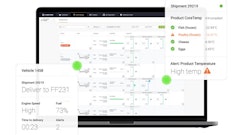
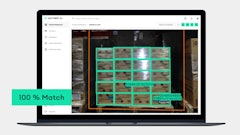
Traceability. The number of U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) food recalls increased more than 30% from Q1 to Q2 2023. As regulations and recalls increasingly impact the food and beverage industry, manufacturers are looking to solutions that provide very granular levels of track and trace capabilities to meet these regulatory requirements and quickly identify the source of an outbreak. For example, cloud-based ERP solutions that can integrate with back-end systems, such as MES and QMS, can pull data from across the enterprise and track ingredients and products from the point of origin to their final destination.
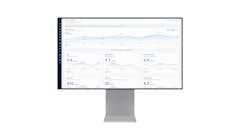
Predictive analytics. Cold food supply chain companies are using predictive analytics to anticipate disruptions and make better decisions. This helps them to reduce waste, improve efficiency and increase customer satisfaction. For example, predictive analytics can be used to predict demand surges, identify potential transportation delays, and forecast the risk of food spoilage.
Food Logistics: Describe some of the challenges impacting many of today’s supply chains.
Bresler: Material shortages, geopolitical issues and natural weather events are some of the most disruptive factors to supply chains. A report on the State of Smart Manufacturing found that supply chain disruptions were among the Top 3 external forces to dampen company growth in 2022. Meanwhile, the shortage and increased prices of raw materials was ranked as the third leading external obstacle to supply chains.
While the cost of raw materials and production of parts may be a benefit to sourcing from faraway regions, it also presents a challenge. Escalating tensions could trigger a conflict destabilizing the flow of raw materials and supplies from the region. Compared to manufacturers that can on-/reshore their supply chain sources, manufacturers that need to manage global supply chains will need to be more agile to adapt to ongoing unpredictable supply chain disruptions. Additionally, businesses need to adapt to evolving regulatory challenges to ensure they’re meeting standards. That’s why “adapting to new regulations and standards” was the ninth leading concern among manufacturers for 2023.
Natural weather occurrences can also have significant impacts on global supply chains, from delays to ruined raw goods. Predicting weather events isn’t impossible, but the increasing severity and frequency of weather events make it much more difficult to plan for.
Food Logistics: Describe the State of Software and Technology, and how AI, robotics and more are shaping the future of the cold food chain.
Bresler: Smart manufacturing technologies and approaches to inventory management enable cold food manufacturers to optimize inventory procurement and supply chain planning, which has a direct impact on revenue generation and cost reduction. In fact, of the smart manufacturing technologies businesses have invested in, process automation produces the biggest ROI according to 33% of companies.
Automation is critical to expanding operations and value in today’s contracting economy and competitive recruitment environment. Time-consuming operations, like inventory purchasing and asset maintenance orders, can be automated to reallocate employee time to focus on more creative and higher value challenges. When organizations automate repeatable tasks, they not only increase productivity but also make jobs at their facilities more attractive to the next generation of workers, who see technology as core to their future and the future of any business.
By leveraging smart manufacturing technology to automate processes, cold food and CPG companies can extract data from their operations and assemble actionable insights to seek opportunities for profitable growth and transform at pace, despite workforce uncertainties. Technology is also helping the industry accelerate their agility and competitive differentiation, serving as an advantage for manufacturers to improve quality, agility, innovation and attract the next generation of talent.
Food Logistics: Looking back at the past 2-3 years, how has the cold food chain progressed? Declined? What’s in store come 2024?
Bresler: From shifting customer demands driven by increased pressure from large-scale competitors and direct-to-consumer trends, the food and beverage industry has faced unprecedented change over the past several years. The pandemic had a massive shift, driving consumers to eat more of their meals (88%) in the home, up from 75% before the pandemic.
Food processors and CPG companies are experiencing a lasting impact from this change. The industry expects to reach $62 billion in the global packaging machinery market by 2030, a 32.7% increase from the estimated market in 2022. Changing consumer demands and preferences are causing manufacturers to work with more SKUs and manage more production information than ever. Additionally, workforce shortages and skills gaps are forcing manufacturers to do more with less. We can continue to see workforce constraints continue in 2024 and will see more smart manufacturing technology permeate the space as a result.
CLICK HERE to read the article in full.